Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Notes Pdf- Human Environment Interactions the Tropical and Subtropical Region
In this post we discuss Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Notes In Class 7th geography ch 8 notes we will learn about the life of people in the different natural regions of the world. You can also download Human Environment Interactions class 7 notes pdf.
People from different parts of the world may look different, but they share the exact basic needs of life – food, clothing and shelter. In class 7 geography ch 8 notes we discuss life in the Amazone Basin and Ganga Brahmputra basin.
Life in the Amazon Basin
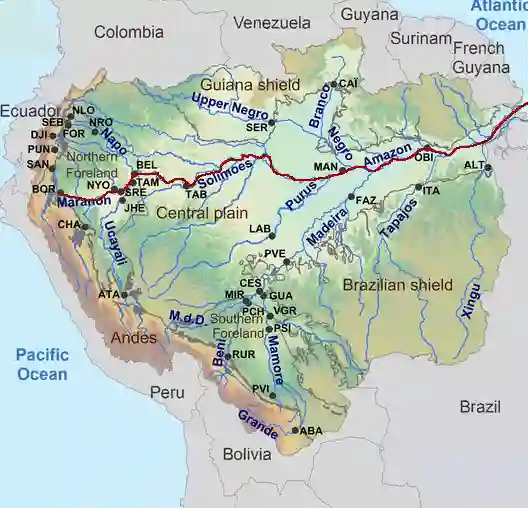
Amazon Basin is a tropical region that lies very close to the equator; between 10°N and 10°S. So, it is referred to as the equatorial region. The river Amazon flows through this region. It flows from the mountains to the west and reaches the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
- The place where a river flows into another body of water is called the river’s mouth.
- Numerous tributaries join the Amazon River to form the Amazon basin.
- The river basin drains portions of Brazil, parts of Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Columbia and a small part of Venezuela.
Climate of Amazon Basin
- Amazon Basin stretches directly on the equator so it is characterized by a hot and wet climate throughout the year.
- Both days and nights are almost equally hot and humid.
- The skin feels sticky.
- It rains almost every day, that too without much warning.
- The day’s temperatures are high with very high humidity.
- At night the temperature goes down but the humidity remains high.
Rain Forest in Amazon Basin
Because of heavy rainfall, thick forests grow. The forests are so thick that the dense “roof” created by leaves and branches does not allow the sunlight to reach the ground.
- The ground remains dark and damp. Only shade-tolerant vegetation may grow here.
- Orchids and bromeliads grow as plant parasites.
- The rainforest is rich in fauna.
- Birds such as toucans, hummingbirds, and birds of paradise are found here.
- bird with their brilliantly coloured plumage and oversized bills for eating makes them different from birds we commonly see in India.
- Animals like monkeys, sloths and ant-eating tapirs are found here.
- Various species of reptiles and snakes such as Crocodiles, snakes, pythons, Anaconda and boa constrictors are some of the species are also thrive in these jungles.
- The basin is home to thousands of species of insects.
- Several species of fishes including the flesh-eating Piranha fish is also found in the river.
Note:- Bromeliads are special plants that store water in their leaves. Animals like frogs use these pockets of water for laying their eggs.
People of the Rainforests
People grow most of their food in small areas after clearing some trees in the forest.
- Men hunt and fish along the rivers, and women care for the crops.
- They mainly grow tapioca, pineapple and sweet potato.
- As hunting and fishing are uncertain it is the women who keep their families alive by feeding them the vegetables they grow.
- They also eat queen ants and egg sacs.
- They practice “slash and burn agriculture”.
- The staple food is manioc, also known as cassava which grows under the ground like the potato.
- Cash crops like coffee, maize and cocoa are also grown.
- The rainforests provide a lot of wood for the houses. Some families live in thatched houses shaped like beehives. There are other large apartment-like houses called “Maloca” with steeply slanting roofs.
The life of the people of the Amazon basin is slowly changing. In the older days, the heart of the forest could
be reached only by navigating the river. Now Trans Amazon highway made all parts of the rainforest accessible. Aircraft and helicopters are also used for reaching various places.
The indigenous population was pushed out of the area and forced to settle in new areas where they continued to practice their distinctive way of farming. The developmental activities are leading to the gradual
destruction of the biologically diverse rainforests.
Ganga Brahmputra Basin
The tributaries of rivers Ganga and Brahmaputra together form the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin in the Indian subcontinent. The basin lies in the sub-tropical region that is situated between 10°N to 30°N latitudes. The tributaries of the River Ganga like the Ghaghra, the Son, the Chambal, the Gandak, the Kosi and the tributaries of Brahmaputra drain it.

The plains of the Ganga and the Brahmaputra, the mountains and the foothills of the Himalayas and the Sundarbans delta are the main features of this basin.
Climate
- Oxbow lakes dot the plain area.
- The area is dominated by a monsoon climate.
- The monsoon brings rains from mid-June to mid-September.
- The summers are hot and the winters are cool.
Topography
The basin area has a varied topography. The environment plays a dominant role in the distribution of the population.
- The mountain areas with steep slopes have inhospitable terrain. Therefore less number of people live in the mountain area.
- The plain area provides the most suitable land for human habitation. The density of the population of the plains is very high.
- Agriculture is the main occupation in the plain area because the soil is fertile.
- Paddy is the main crop. Wheat, maize, sorghum, gram and millet are the other crops grown.
- Cash crops like sugarcane and jute are also grown. Banana plantations are seen in some areas of the plain.
- In West Bengal and Assam tea is grown in plantations.
- Silk is produced through the cultivation of silkworms in parts of Bihar and Assam.
- In the mountains and hills, where the slopes are gentle, crops are grown on terraces.
Vegetation
The vegetation cover of the area varies according to the type of landforms. In the Ganga and Brahmaputra plains tropical deciduous trees grow, along with teak, sal and peepal.
- Thick bamboo groves are common in the Brahmaputra plain.
- The delta area is covered with mangrove forests.
- In parts of Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh, coniferous trees like pine, deodar and fir can be seen because the climate is cool and the slopes are steep.
Wildlife
There is a variety of wildlife in the basin.
- Elephants, tigers, deer and monkeys are common animals.
- The one-horned rhinoceros is found in the Brahmaputra plain.
- In the delta area, Bengal tigers, crocodiles and alligators are found.
- Aquatic life abounds in the fresh river waters, the lakes and the Bay of Bengal Sea.
- The most popular varieties of fish are the rohu, catla and hilsa.
- Fish and rice are the staple diet of the people living in the area.
Town and Cities
The Ganga-Brahmaputra plain has several big towns and cities.
- The cities of Allahabad, Kanpur, Varanasi, Lucknow, Patna and Kolkata all with a population of more than ten lakhs are located along the River Ganga
- The wastewater from these towns and industries is discharged into the rivers. This leads to the pollution of the rivers.
Transportation
All four ways of transport are well developed in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. In plain areas, roadways and railways transport people from one place to another. The waterways are an effective means of transport, particularly along the rivers.
Tourism Centres
Tourism is another important activity of the basin.
Some important places are- the Taj Mahal, Allahabad, Buddhist stupas, Imambara, Kaziranga and Manas wildlife sanctuaries etc.
Some Important places on the bank of the river.
We hope you like Class 7 Geography Chapter 8 Notes Please share this post Class 7 Geography Ch 8 Notes pdf with your friends.
You may also like to read